Meningitis - Causes, Ways Of Dispersion & Precautionary Measures

Meningitis is a serious illness that can be life threatening. Although the federal ministry of health has advised Nigerians to remain calm as it is working to put an end to the spread of the epidemic, it is important that every Nigerian is made aware of the health risk posed by the disease.
Did you know? You can comment on this post! Just scroll down
Boade Akinola the director media and public relations at the federal ministry of health said that although, “this is not the first time or the worst epidemic ever faced by Nigeria, this round of the epidemic has come with a difference, as all previous epidemics were caused by Neisseria Meningitides type ‘A’, but this year we are recording Neisseria Meningitides type C in epidemic proportion for the first time.”
WHAT IS MENINGITIS?
Meningococcal meningitis is a serious bacterial infection. It affects the protective lining of the brain and the spinal cord or “meninges.”
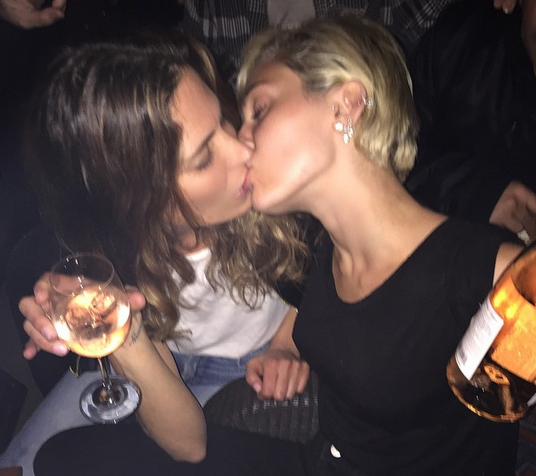
It is usually spread via saliva or mucus. Kissing, living in close or communal spaces, or sharing cups and eating utensils are all ways to get the infection.
The most common causes of meningitis are viral and bacterial infections. Other causes may include cancer, chemical irritation, fungi, and drug allergies.
The most common kinds are viral and bacterial meningitis both contagious and can be transmitted by coughing, sneezing, or close contact.
VIRAL MENINGITIS
According to Healthline, a health journal, viral meningitis is the most common type of meningitis. Viruses in the Enterovirus category cause 85 percent of cases.
Viruses in the Enterovirus category cause about 10 to 15 million infections per year, but only a small percentage of people who get infected will develop meningitis. Viral meningitis typically goes away without treatment.
It is usually spread via saliva or mucus. Kissing, living in close or communal spaces, or sharing cups and eating utensils are all ways to get the infection.
The most common causes of meningitis are viral and bacterial infections. Other causes may include cancer, chemical irritation, fungi, and drug allergies.
The most common kinds are viral and bacterial meningitis both contagious and can be transmitted by coughing, sneezing, or close contact.
VIRAL MENINGITIS
According to Healthline, a health journal, viral meningitis is the most common type of meningitis. Viruses in the Enterovirus category cause 85 percent of cases.
Viruses in the Enterovirus category cause about 10 to 15 million infections per year, but only a small percentage of people who get infected will develop meningitis. Viral meningitis typically goes away without treatment.
FUNGAL MENINGITIS
Fungal meningitis is rare and usually caused by fungus spreading through blood to the spinal cord. Although anyone can get fungal meningitis, people with weakened immune systems, like those with an HIV infection or cancer, are at increased risk.
The most common cause of fungal meningitis for people with weak immune systems is Cryptococcus. This disease is one of the most common causes of adult meningitis in Africa.
HOW IT SPREADS
Fungal meningitis is not spread from person to person. Fungal meningitis can develop after a fungus spreads through the bloodstream from somewhere else in the body to the brain or spinal cord or from an infection next to the brain or spinal cord.
BACTERIAL MENINGITIS
Bacterial meningitis is contagious and caused by infection from certain bacteria. The medical journals warns that it is fatal if left untreated between 5 to 40 percent of children and 20 to 50 percent of adults with this condition die.
Prolonged close contact with an infected person may increase risk of transmission. This is a concern in day care centres, schools, and college dormitories.
The bacteria can also spread through saliva, mucus, kissing, sharing eating utensils, coughing, sneezing, and contaminated food
Medical experts say a lot of people have meningitis-causing bacteria in their throats or noses, even if they do not get sick, they can still spread it to others.
According to the World Health Organization, the incubation period is between two and 10 days. The largest concentration of meningococcal disease is in sub-Saharan Africa.
The US Center for diseases control (CDC), estimates that about 4,100 cases of bacterial meningitis are reported each year in the United States.
Common symptoms of meningitis include sudden high fever and chills, headache, stiff neck, purple areas on the skin that look like bruises. The symptoms usually come on suddenly, within one week of being exposed to the bacteria.
Other less common symptoms of meningitis are confusion, particularly in older adults, nausea and vomiting, sensitivity to light, rash, usually a symptom appearing during later stages, drowsiness and fatigue, seizure, coma.
Children tend to display different symptoms of meningitis than adults and they include irritability, partial seizures, red or purple rashlike areas on the skin, projectile vomiting, difficulty with feeding, high-pitched crying.
REDUCING THE RISK OF MENINGITIS
Common precautions medical practitioners advise are regular washing of hands with warm water and soap before eating, after using the toilet, after changing a diaper, or after tending to someone who is ill.
They further counsel against sharing eating utensils, straws, or plates and maintain hygiene as regards covering nose and mouth when coughing or sneezing.
Parents are also urged to stay up to date with immunizations and booster shots for meningitis and seek immediate medical help when a child exhibits symptoms.
Article Posted 7 Years ago. You can post your own articles and it will be published for free.
No Registration is required! But we review before publishing! Click here to get started
One Favour Please! Subscribe To Our YouTube Channel!
468k
Cook Amazing Nigerian Dishes, Follow Adorable Kitchen YouTube Channel!
1.1m
Like us on Facebook, Follow on Twitter
React and Comment
Click Here To Hide More Posts Like This
Watch and Download Free Mobile Movies, Read entertainment news and reports, Download music and Upload your own For FREE.
Submit Your Content to be published for you FREE! We thrive on user-submitted content!
But we moderate!